Latest news & events from CRUK MI
All the latest news and updates from across the Institute
Latest news & events from CRUK MI
All the latest news and updates from across the Institute
Prizes, activities, events and more
See all the latest news from across our research teams, core facilities and staff. Use the search bar to select news items by category or date
News, Staff News
Professor Samra Turajlić appointed as Institute Director
18 June 2025
We are delighted to announce, along with Cancer Research UK, The University of Manchester and The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, the appointment of Professor Samra Turajlić as our new Institute Director.
Topics & Tags
Staff News
18 June 2025
Research Publication
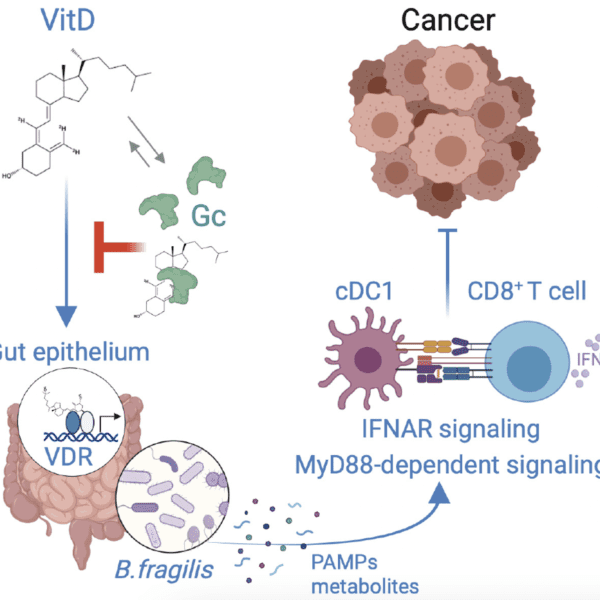
Cancer Inflammation and Immunity group publish exciting research in Cancer Discovery
20 October 2025
Topics & Tags
Immunotherapy | Skin Cancer
20 October 2025
News, Funding success, Staff News
Justin Loke appointed to Amit Patel Leukaemia Research Fellowship
28 August 2025
Topics & Tags
Amit Patel Leukaemia Research Fellowship | Blood Cancer | Leukaemia
28 August 2025
News, Research Engagement
Research Engagement Activities – How We Study Cancer
21 August 2025
We have developed research engagement activities which help explain how and why we use mice in some of our research, and new developments that can reduce or replacing mice in some experiments
Topics & Tags
AWERB | Culture of Care | Animal Models
21 August 2025
News, Funding success
Luciano Nicosia receives Blood Cancer UK Early Career Advancement Fellowship
6 August 2025
Dr Luciano Nicosia has been awarded a 3-year Early Career Advancement Fellowship with Blood Cancer UK.
Topics & Tags
Award | acute myeloid leukemia (AML) | Blood Cancer | Staff News
6 August 2025
Staff News, Events, News
Institute launches Hidden Disabilities Sunflower campaign
23 July 2025
This Tuesday 22nd July saw the launch of the Institute’s Hidden Disabilities Sunflower campaign. The Hidden Disabilities Sunflower is a globally recognised symbol for individuals with non-visible disabilities. Not all disabilities are visible, conditions such as autism, chronic pain, mental health conditions, hearing loss, or mobility issues may be hidden.
Topics & Tags
Hidden Disabilities | Human Resources
23 July 2025
News, Staff News
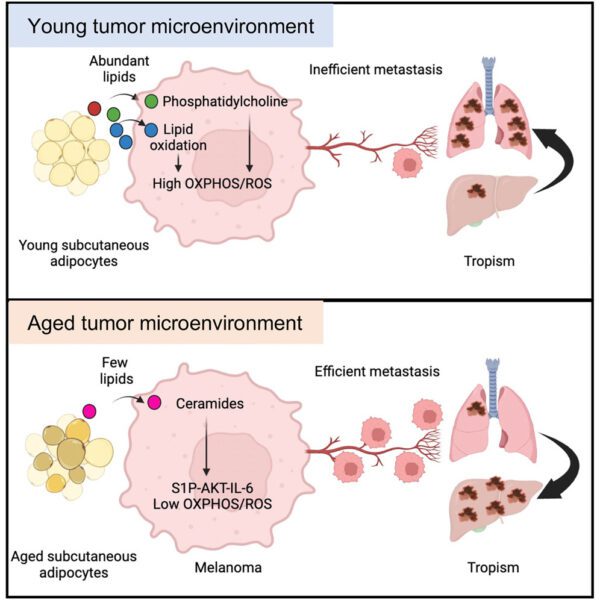
Dr Amaya Viros: Working towards a skin cancer-free future
23 July 2025
Dr Amaya Viros, head of Skin Cancer and Ageing, spoke to The Telegraph newspaper for an article “Working towards a skin cancer-free future” which explores how Dr Viros and her team aim to understand and prevent the spread of cancer in different patients.
Topics & Tags
Interview | Personalised medicine | Skin Cancer
23 July 2025
Our Research
Our research spans the whole spectrum of cancer research from cell biology through to translational and clinical studies
Research Groups
Our research groups study many fundamental questions of cancer biology and treatment
Our Facilities
The Institute has outstanding core facilities that offer cutting edge instruments and tailored services from expert staff
Latest News & Updates
Find out all our latest news
Careers that have a lasting impact on cancer research and patient care
We are always on the lookout for talented and motivated people to join us. Whether your background is in biological or chemical sciences, mathematics or finance, computer science or logistics, use the links below to see roles across the Institute in our core facilities, operations teams, research groups, and studentships within our exceptional graduate programme.