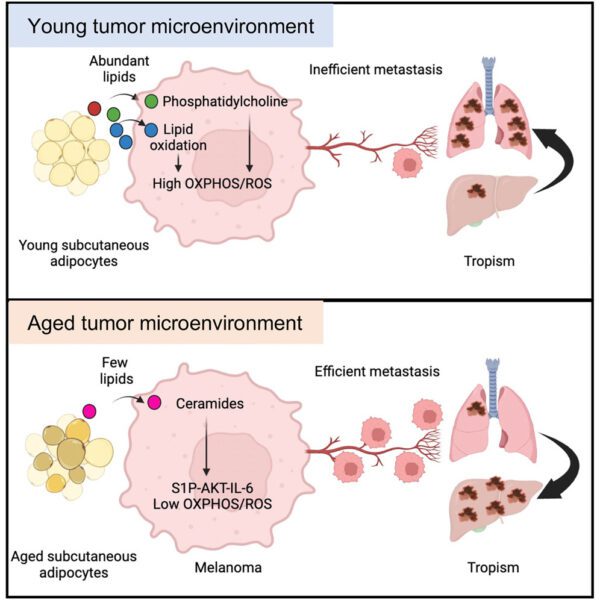
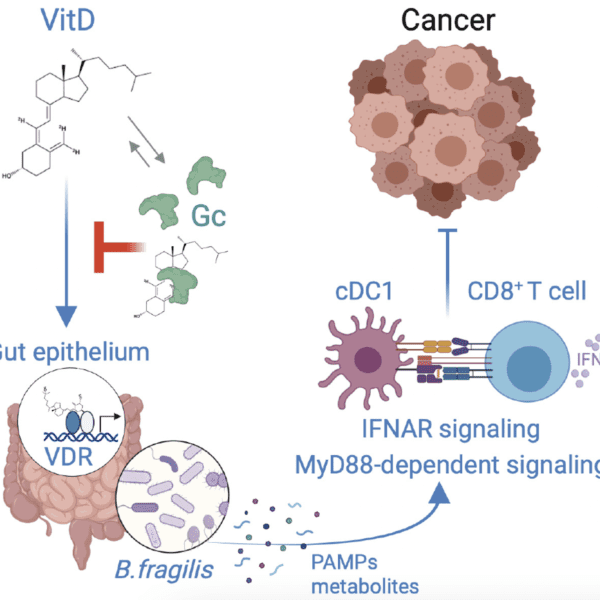
Article highlights & insights
Fluctuations in TOR, AMPK and MAP-kinase signalling maintain cellular homeostasis and coordinate growth and division with environmental context. We have applied quantitative, SILAC mass spectrometry to map TOR and nutrient-controlled signalling in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Phosphorylation levels at more than 1000 sites were altered following nitrogen stress or Torin1 inhibition of the TORC1 and TORC2 networks that comprise TOR signalling. One hundred and thirty of these sites were regulated by both perturbations, and the majority of these (119) new targets have not previously been linked to either nutritional or TOR control in either yeasts or humans.
Elimination of AMPK inhibition of TORC1, by removal of AMPKα (ssp2::ura4+), identified phosphosites where nitrogen stress-induced changes were independent of TOR control. Using a yeast strain with an ATP analogue-sensitized Cdc2 kinase, we excluded sites that were changed as an indirect consequence of mitotic control modulation by nitrogen stress or TOR signalling. Nutritional control of gene expression was reflected in multiple targets in RNA metabolism, while significant modulation of actin cytoskeletal components points to adaptations in morphogenesis and cell integrity networks. Reduced phosphorylation of the MAPKK Byr1, at a site whose human equivalent controls docking between MEK and ERK, prevented sexual differentiation when resources were sparse but not eliminated.
Fluctuations in TOR, AMPK and MAP-kinase signalling maintain cellular homeostasis and coordinate growth and division with environmental context. We have applied quantitative, SILAC mass spectrometry to map TOR and nutrient-controlled signalling in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Phosphorylation levels at more than 1000 sites were altered following nitrogen stress or Torin1 inhibition of the TORC1 and TORC2 networks that comprise TOR signalling. One hundred and thirty of these sites were regulated by both perturbations, and the majority of these (119) new targets have not previously been linked to either nutritional or TOR control in either yeasts or humans.
Elimination of AMPK inhibition of TORC1, by removal of AMPKα (ssp2::ura4+), identified phosphosites where nitrogen stress-induced changes were independent of TOR control. Using a yeast strain with an ATP analogue-sensitized Cdc2 kinase, we excluded sites that were changed as an indirect consequence of mitotic control modulation by nitrogen stress or TOR signalling. Nutritional control of gene expression was reflected in multiple targets in RNA metabolism, while significant modulation of actin cytoskeletal components points to adaptations in morphogenesis and cell integrity networks. Reduced phosphorylation of the MAPKK Byr1, at a site whose human equivalent controls docking between MEK and ERK, prevented sexual differentiation when resources were sparse but not eliminated.
Institute Authors
Groups
Group leader
Grants
This work was supported by Cancer Research UK.
Meet the Research Team

Senior Group Leader

Senior Scientific Officer
Our Research
Our research spans the whole spectrum of cancer research from cell biology through to translational and clinical studies
Research Groups
Our research groups study many fundamental questions of cancer biology and treatment
Our Facilities
The Institute has outstanding core facilities that offer cutting edge instruments and tailored services from expert staff
Latest News & Updates
Find out all our latest news
Careers that have a lasting impact on cancer research and patient care
We are always on the lookout for talented and motivated people to join us. Whether your background is in biological or chemical sciences, mathematics or finance, computer science or logistics, use the links below to see roles across the Institute in our core facilities, operations teams, research groups, and studentships within our exceptional graduate programme.