Article highlights & insights
Prostate cancer (PCa) is a clinically heterogeneous disease and has poor patient outcome when tumours progress to castration-resistant and metastatic states. Understanding the mechanistic basis for transition to late stage aggressive disease is vital for both assigning patient risk status in the localised setting and also identifying novel treatment strategies to prevent progression. Subregions of intratumoral hypoxia are found in all solid tumours and are associated with many biologic drivers of tumour progression.
Crucially, more recent findings show the co-presence of hypoxia and genomic instability can confer a uniquely adverse prognosis in localised PCa patients. In-depth informatic and functional studies suggests a role for hypoxia in co-operating with oncogenic drivers (e.g. loss of PTEN) and suppressing DNA repair capacity to alter clonal evolution due to an aggressive mutator phenotype. More specifically, hypoxic suppression of homologous recombination represents a “contextual lethal” vulnerability in hypoxic prostate tumours which could extend the application of existing DNA repair targeting agents such as poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors.
Further investigation is now required to assess this relationship on the background of existing genomic alterations relevant to PCa, and also characterise the role of hypoxia in driving early metastatic spread. On this basis, PCa patients with hypoxic tumours can be better stratified into risk categories and treated with appropriate therapies to prevent progression.
Prostate cancer (PCa) is a clinically heterogeneous disease and has poor patient outcome when tumours progress to castration-resistant and metastatic states. Understanding the mechanistic basis for transition to late stage aggressive disease is vital for both assigning patient risk status in the localised setting and also identifying novel treatment strategies to prevent progression. Subregions of intratumoral hypoxia are found in all solid tumours and are associated with many biologic drivers of tumour progression.
Crucially, more recent findings show the co-presence of hypoxia and genomic instability can confer a uniquely adverse prognosis in localised PCa patients. In-depth informatic and functional studies suggests a role for hypoxia in co-operating with oncogenic drivers (e.g. loss of PTEN) and suppressing DNA repair capacity to alter clonal evolution due to an aggressive mutator phenotype. More specifically, hypoxic suppression of homologous recombination represents a “contextual lethal” vulnerability in hypoxic prostate tumours which could extend the application of existing DNA repair targeting agents such as poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitors.
Further investigation is now required to assess this relationship on the background of existing genomic alterations relevant to PCa, and also characterise the role of hypoxia in driving early metastatic spread. On this basis, PCa patients with hypoxic tumours can be better stratified into risk categories and treated with appropriate therapies to prevent progression.
Institute Authors
Groups
Group leader
Research topics & keywords
All publications
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-025-02582-x
Mutant p53 induces SH3BGRL expression to promote cell engulfment
1 July 2025
Institute Authors (5)
Garry Ashton, John Weightman, Wolfgang Breitwieser, Sudhakar Sahoo, Antonia Banyard
Labs & Facilities
Computational Biology Support, Flow Cytometry, Molecular Biology
1 July 2025
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115603
Functional characterisation of the ATOH1 molecular subtype indicates a pro-metastatic role in small cell lung cancer
27 May 2025
Institute Authors (2)
Caroline Dive, Kathryn Simpson
Research Group
Small Cell Lung Cancer Biology
27 May 2025
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2025.04.001
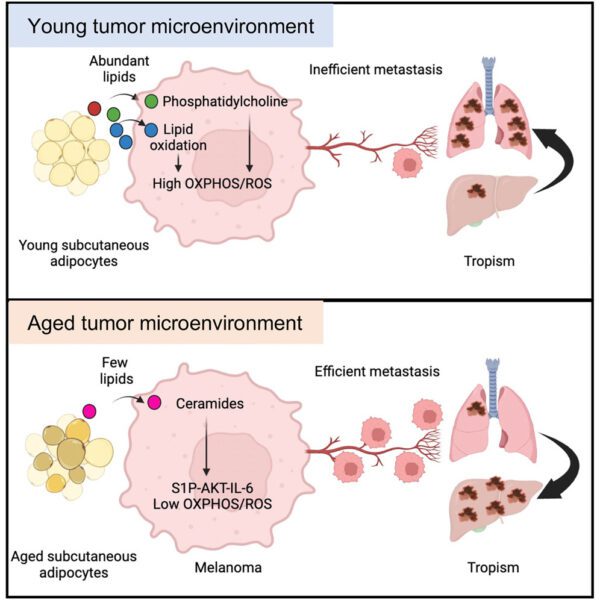
Stromal lipid species dictate melanoma metastasis and tropism
24 April 2025
Institute Authors (5)
Amaya Viros, Duncan Smith, Garry Ashton, Alex Baker, Tim Somervaille
Labs & Facilities
Biological Mass Spectrometry, Histology, Visualisation, Irradiation and Analysis
Research Group
Skin Cancer & Ageing
24 April 2025
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58343-y
A human model to deconvolve genotype-phenotype causations in lung squamous cell carcinoma
4 April 2025
Institute Authors (4)
Carlos Lopez-Garcia, Robert Sellers, Sudhakar Sahoo, Caroline Dive
Labs & Facilities
Computational Biology Support
Research Group
Translational Lung Cancer Biology
4 April 2025
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-024-02157-x
The PI3K-AKT-mTOR axis persists as a therapeutic dependency in KRASG12D-driven non-small cell lung cancer
12 November 2024
Institute Authors (1)
Amaya Viros
Labs & Facilities
Genome Editing and Mouse Models
Research Group
Skin Cancer & Ageing
12 November 2024
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-024-01610-0
The small inhibitor WM-1119 effectively targets KAT6A-rearranged AML, but not KMT2A-rearranged AML, despite shared KAT6 genetic dependency
8 October 2024
Institute Authors (6)
Georges Lacaud, Mathew Sheridan, Michael Lie-a-ling, Liam Clayfield, Jessica Whittle, Jingru Xu
Research Group
Stem Cell Biology
8 October 2024
Our Research
Our research spans the whole spectrum of cancer research from cell biology through to translational and clinical studies
Research Groups
Our research groups study many fundamental questions of cancer biology and treatment
Our Facilities
The Institute has outstanding core facilities that offer cutting edge instruments and tailored services from expert staff
Latest News & Updates
Find out all our latest news